
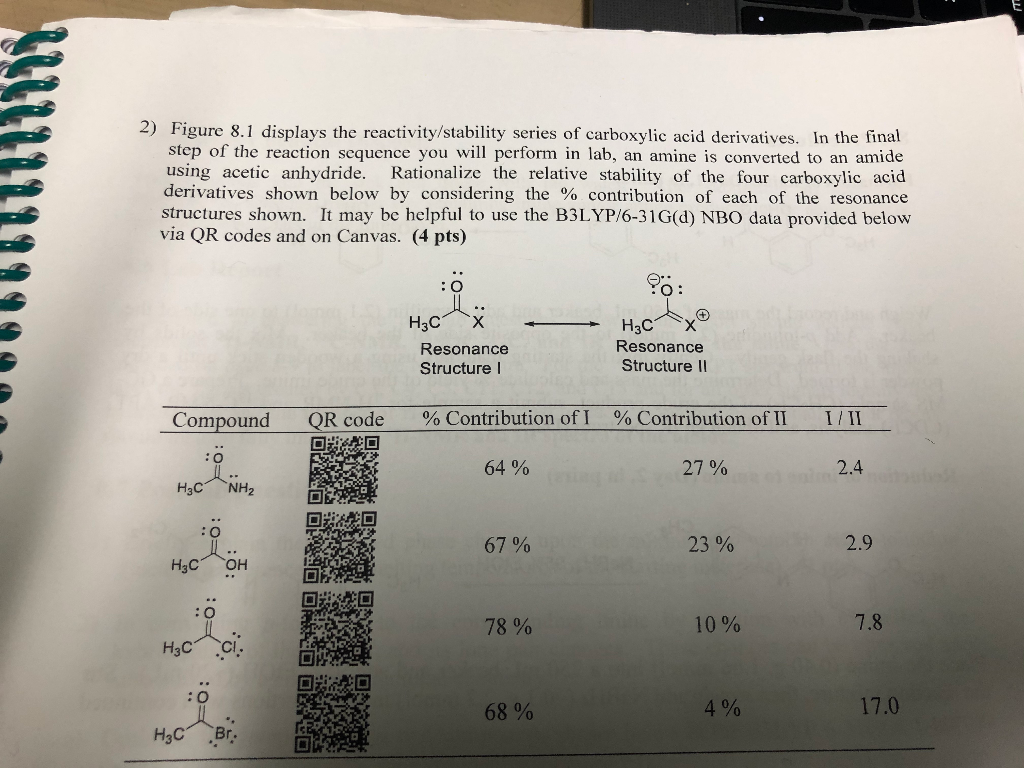
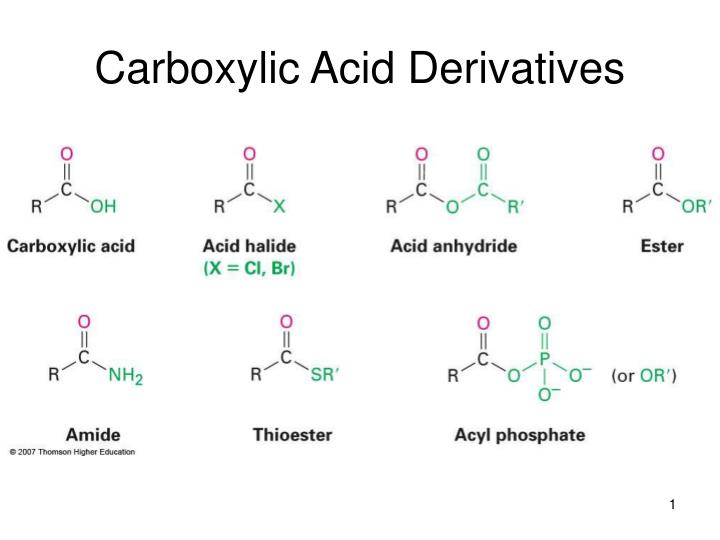
the kidney must work very hard to excrete the excessive levels of bivalent ions in the ocean water, causing kidney failure.the water has a very low solute concentration relative to the body’s cells, resulting in cell swelling and death.So that all meshes together very nicely and tells us the correct answer is D.ĭrinking ocean water is ultimately fatal to a human because: Those are two very common contributors to resonance. And then remembering what the peptide bond has which is carbonyl carbon and nitrogen with a lone pair. Resonance gives a more stable compound so resonance stabilization is a thing in and of itself. There are lots of places for electrons to move around resonance structures, and having more than one of them typically indicates stability. But if you look at it, resonance stabilization makes sense. So C is out.ĭ – Just by the process of elimination, this is the correct answer. So this is just the opposite of everything. Not proteins are unstable because peptide bonds are unstable. Now, the point of the question is that proteins are stable because peptide bonds are stable. So B is out.Ĭ – This is giving us the opposite of what we want. The carboxylic acid derivative is not a marker of stability, but a marker of reactivity. Thinking back to your chemistry, no acid halides are super reactive. That’s the carboxy terminus of the amino acid. And for this reason, we cross out A.ī – there is a carboxylic acid involved in a peptide bond. Then both carbon and nitrogen are involved in the bond are bonded to two other things. And so, you know that you’re going to not have a triple bond, right off the bat. It’s an amide linkage which is a peptide bond.Ī – You might actually want to draw it out just so you can see what it looks like. Then you’re going to lose a molecule of water, and you’re going to get a bond between your C and N. So it’s the C=OH on one end and the NH2 on the other. would result in proteins that denatured easily if it were unstable.Ī peptide bond is an amide linkage between the anion group of one and the carboxylic acid group of another.consists of a triple bond, which is significantly stronger and more stable.The peptide bond that forms the backbone of proteins is especially stable because it: So you’re going into pure knowledge mode and pure recall. Then when you get to the discrete, the course is leveling out a bit. So you’re in a hill-running mode when you’re on a passage. Hills would be the reading comprehension passages in the sciences, for some students, because they find that passages are harder than discrete questions. Because you will be running differently when you’re on flat ground versus when you’re on a hill. Joya advises in handling discrete questions is to treat it the way you treat running. So you usually see three to four questions per passage, and three to four discrete questions per discrete chunk. And it’s usually the same number of discrete questions as you would have in a passive question. This is true for Chem/Phys and psych/social as well. Generally, there are usually two discrete groups in the science passages. Listen to this podcast episode with the player above, or keep reading for the highlights and takeaway points. If you would like to follow along on YouTube, go to. We’re joined by Joya from Blueprint MCAT, formerly Next Step Test Prep. We evaluate peptide bonds, solute concentrations, gene transcriptions, and more! In this episode, we tackle the first bio/biochem discrete question set. Apple Podcasts | Google Podcasts Session 212


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
